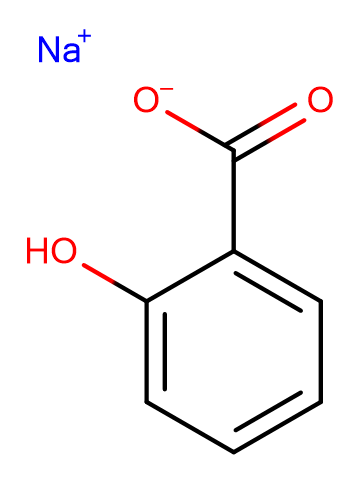
Sodium salicylate
CAS No. 54-21-7
Sodium salicylate( Sodium salicylate | Kerasalicyl | Kerosal | Magsalyl )
Catalog No. M14942 CAS No. 54-21-7
Sodium salicylate is a metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid, and functions by inhibiting NF-kB and reduces oxidative stress.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 41 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSodium salicylate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSodium salicylate is a metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid, and functions by inhibiting NF-kB and reduces oxidative stress.
-
DescriptionSodium salicylate is a metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid, and functions by inhibiting NF-kB and reduces oxidative stress.(In Vitro):Sodium Salicylate is an effective inhibitor of COX-2 activity at concentrations far below those required to inhibit NF-κB (20 mg/mL) activation. Sodium Salicylate inhibits prostaglandin E2 release when add together with interleukin 1β for 24 hr with an IC50 value of 5 μg/mL, an effect that is independent of NF-κB activation or COX-2 transcription or translation. Sodium Salicylate acutely (30 min) also causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of COX-2 activity measured in the presence of 0, 1, or 10 μM exogenous arachidonic acid. In contrast, when exogenous arachidonic acid is increased to 30 μM, Sodium Salicylate is a very weak inhibitor of COX-2 activity with an IC50 of >100 μg/mL. When added together with IL-1β for 24 hr, Sodium Salicylate causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of PGE2 release with an apparent IC50 value of approximately 5 μg/mL. The ability of Sodium Salicylate to directly inhibit COX-2 activity in A549 cells is tested after a 30-min exposure period, followed by the addition of different concentrations of exogenous arachidonic acid (1, 10, and 30 μM). Sodium Salicylate causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of COX-2 activity in the absence of added arachidonic acid or in the presence of 1 or 10 μM exogenous substrate with an apparent IC50 value of approximately 5 μg/mL. However, when the same experiments are performed using 30 μM arachidonic acid, Sodium Salicylate is an ineffective inhibitor of COX-2 activity, with an apparent IC50 value of more than 100 μg/mL, and achieves a maximal inhibition of less than 50%.(In Vivo):In C57Bl/6 DIO mice, Salicylate decreases both fasting and postprandial plasma glucose levels. Furthermore, there is a trend to reduce plasma triglyceride levels after Salicylate treatment in C57Bl/6 DIO mice (P=0.059). Salicylate significantly reduces 11β-HSD1 mRNA in omental adipose tissue in C57Bl/6 DIO mice, with a similar trend in mesenteric adipose (P=0.057). In mesenteric adipose of C57Bl/6 DIO mice, Salicylate also reduces 11β-HSD1 enzyme activity.
-
In VitroSodium Salicylate is an effective inhibitor of COX-2 activity at concentrations far below those required to inhibit NF-κB (20 mg/mL) activation. Sodium Salicylate inhibits prostaglandin E2 release when add together with interleukin 1β for 24 hr with an IC50 value of 5 μg/mL, an effect that is independent of NF-κB activation or COX-2 transcription or translation. Sodium Salicylate acutely (30 min) also causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of COX-2 activity measured in the presence of 0, 1, or 10 μM exogenous arachidonic acid. In contrast, when exogenous arachidonic acid is increased to 30 μM, Sodium Salicylate is a very weak inhibitor of COX-2 activity with an IC50 of >100 μg/mL. When added together with IL-1β for 24 hr, Sodium Salicylate causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of PGE2 release with an apparent IC50 value of approximately 5 μg/mL. The ability of Sodium Salicylate to directly inhibit COX-2 activity in A549 cells is tested after a 30-min exposure period, followed by the addition of different concentrations of exogenous arachidonic acid (1, 10, and 30 μM). Sodium Salicylate causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of COX-2 activity in the absence of added arachidonic acid or in the presence of 1 or 10 μM exogenous substrate with an apparent IC50 value of approximately 5 μg/mL. However, when the same experiments are performed using 30 μM arachidonic acid, Sodium Salicylate is an ineffective inhibitor of COX-2 activity, with an apparent IC50 value of more than 100 μg/mL, and achieves a maximal inhibition of less than 50%.
-
In VivoIn C57Bl/6 DIO mice, Salicylate decreases both fasting and postprandial plasma glucose levels. Furthermore, there is a trend to reduce plasma triglyceride levels after Salicylate treatment in C57Bl/6 DIO mice (P=0.059). Salicylate significantly reduces 11β-HSD1 mRNA in omental adipose tissue in C57Bl/6 DIO mice, with a similar trend in mesenteric adipose (P=0.057). In mesenteric adipose of C57Bl/6 DIO mice, Salicylate also reduces 11β-HSD1 enzyme activity.
-
SynonymsSodium salicylate | Kerasalicyl | Kerosal | Magsalyl
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetCOX
-
RecptorCOX-1| COX-3| NF-κB
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number54-21-7
-
Formula Weight160.11
-
Molecular FormulaC7H5NaO3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater: 32 mg/mL (198.62 mM); DMSO: 32 mg/mL (198.62 mM)
-
SMILESO=C([O-])C1=CC=CC=C1O.[Na+]
-
Chemical NameBenzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, monosodium salt
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Kopp E, et al. Science, 1994, 265(5174), 956-959.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Nepodin
Nepodin has antimalarial, and anti-inflammatory activities, it shows significant cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitory activity.
-
SC57666
SC57666 is a highly selective COX2 inhibitor (IC50 at 26 nM) that shows no activity against COX1.
-
Ebselen
Ebselen is a mimic of glutathione peroxidase and can also react with peroxynitrite.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


